What is an Asset Class? Understanding Capital Markets

- Asset classes are groupings of investments with similar characteristics.
- Each asset class has its own risk and reward dynamic; investors often diversify these.
- Common asset classes include equities, fixed income, FX, and alternatives.
- As of 31.12.2023, equities were the largest asset class in the world at USD 175tn notional value.
- Valuations and liquidity vary based on asset and market conditions; historic assumptions may not be reliable.
What is an Asset Class?
Asset classes are groupings of investments with similar characteristics in terms of structure, risk, and reward.
By grouping investments, it is easier to understand their absolute and relative returns.
There may be no correlation between the asset classes; however, investors may rotate between them based on returns, market conditions, or investment goals. Others may diversify across the asset classes.
What are the main Asset Classes?
The most common asset classes are cash, fixed income, equities, FX, commodities, alternatives, and digital assets (it is common to list asset classes from lowest to highest risk).
In some asset classes, the investment will be listed on a public exchange or market, while in others it is a private or over the counter (OTC) transaction.
What size are global Capital Markets?
Valuations in public capital markets are dynamic, while in private markets they are opaque and often subjective. The largest asset classes in capital markets by notional outstanding are:
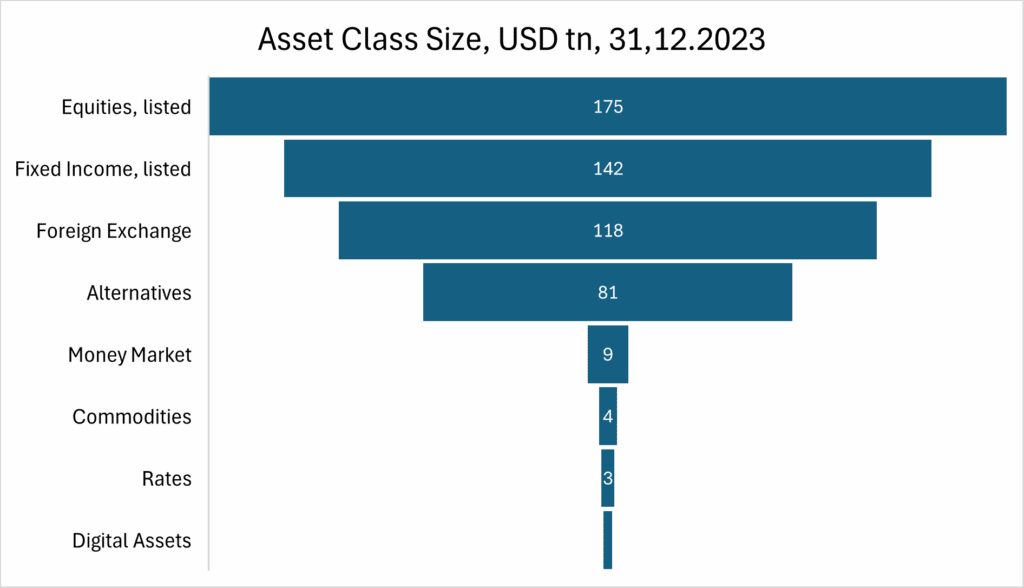
Equities Asset Class
Description: Shares in a company that is publicly listed.
Typology: Ordinary, preference, class, non-voting, etc.
Liquidity: High, subject to how much of the company is floated, volumes, market, etc.
Returns: Appreciation of value and dividend payments (cash or shares).
Risk: Company performance and market risk.
Fixed Income Asset Class
Description: Bonds of a corporate or financial institution that are publicly listed.
Typology: Fixed, floating, zero-coupon, convertible, callable, put, etc.
Liquidity: High, subject to the size of issue, volumes, market, etc.
Returns: Appreciation of value and fixed payment of capital and interest. Equity if convertible.
Risk: Counterparty credit and market risk. Typically rated, but care is required on creditor ranking.
Money Market Asset Class
Description: Accounts and fixed income instruments with very short-term maturities.
Typology: MM account, commercial paper (corporate), treasury bills (government).
Liquidity: High, if traded, it depends on the size of the issue, volumes, market, etc.
Returns: Fixed payment of capital and interest.
Risk: Counterparty credit.
Foreign Exchange Asset Class
Description: Trading of foreign currencies, of which 99% happens over the counter (OTC).
Typology: Spot, forward, option, future.
Liquidity: Depends on currency pairs.
Returns: Appreciation of value.
Risk: Counterparty credit, settlement, and market risk. Higher risks may be collateralised.
Commodities Asset Class
Description: Trading of commodities on a listed exchange or traded over the counter (OTC).
Typology: Energy, metals (base, precious, industrial), agricultural, Livestock, spot, future, option.
Liquidity: Depends on the commodity and market.
Returns: Appreciation of value.
Risk: Counterparty credit, settlement, and market risk. Higher risks may be collateralised.
Alternatives Asset Class
Description: Non-standard asset types, traded in private markets, and often held over a long term.
Typology: Private Equity, Private Debt, Real Estate, Collectibles, Infrastructure.
Liquidity: Low or very low, depending on matching buyer and seller.
Returns: Private Debt is a fixed payment of capital and interest. Real Estate provides an income stream (yield). Others are appreciation of value, which in some cases can be high.
Risk: Complex and dependent on each situation, but typically liquidity, counterparty credit, and market risk. In some cases, alternatives also have little transparency or regulation.
Rates Asset Class
Description: Bonds of a government that are publicly listed or traded over the counter (OTC).
Typology: Sovereign, inflation-linked, IR swap, IR option, repo, etc.
Liquidity: High, depends on the size of the issue, volumes, market, etc.
Returns: Appreciation of value if bond, fixed payment of capital and interest.
Risk: Counterparty credit and market risk. Typically rated, but care is required on creditor ranking.
Digital Assets
Description: digital assets that are publicly listed.
Typology: Cryptocurrency, stablecoins, NFTs.
Liquidity: Variable, depends on volume, market, etc.
Returns: Appreciation of value.
Risk: Market risk and fraud risk. In some cases, highly volatile, with little transparency or regulation.
Cash and Equivalents
Description: cash held in a bank, e-money, or investment account.
Typology: Cash, deposit, certificate of deposit.
Liquidity: Very high, although some deposits are subject to a minimum term.
Returns: Low, depends on prevailing interest rates.
Risk: Counterparty credit risk, may be subject to a guarantee or insurance.


