Core Banking providers in Europe: Digital financial services

- Core banking systems are the go-to infrastructure for banks, PSPs and FinTechs.
- Next-generation core systems are low/no code, cloud-native, and API-first.
- Proven benefits include better time-to-market, client engagement, efficiency and agility.
- Next-generation core banking providers capture market share and private equity funding.
- Sure tracks 50 providers in the European core banking sector.
What is a Core Banking system?
Core Banking systems are the critical infrastructure used to run Banks, PSPs, and FinTechs. Systems have different capabilities but are generally broad in coverage: multi-tenant, asset-class, currency, and payment-rail.
Core systems have strengths in customer management, transaction processing, service charge and interest calculation, general ledger accounting, reporting to regualtors and management. Other modules may include channel management, decisioning, and risk management.
Core systems possess robust configuration capabilities for products, prices, workflows, business rules, and user management. A full audit trail of user and client activity helps users demonstrate governance and compliance.
What is next generation Core Banking?
Banking technology has evolved over 15 years, from monolithic, on-premise solutions to low/no code, cloud-native, API-first platforms.
This allows users to compose the components they need, from single product to full bank, scale faster, and adapt as requirements change.
Omni-channel processing occurs at high volume and in real-time, while APIs to RegTech and client engagement tools support end-to-end process automation.
Digitisation of processes unlocks data-driven insights on client needs and business performance. As Artificial Intelligence advances, new analytics and automation opportunities will emerge.
SaaS models simplify infrastructure and operations, reduce deployment effort, make spend more usage-based and reduce vendor lock.
Use cases for next generation Core Banking?
Core Banking Transformation: Migration to a cloud-native platform that is faster and more efficient.
Client Onboarding: Run AML/CTF checks, open current and deposit accounts.
Loan Automation: Automate the loan life cycle across credit scoring, disbursement, limit management, collateral, collection, NPLs, and reporting.
Payments Hub: Connect to banks, cards, payment rails, and wallets with a single API, and process pay in/out in real-time.
Markets: Trade in real-time and manage portfolios across FX, Fixed Income, and other asset classes.
StartUps: Launch quickly and economically with ready solutions and APIs.
GRC: Embed business rules into workflows, score clients and transactions, run analytics, and report to regulators.
What are the benefits of Core Banking?
Client Centricity: Deep insights on clients helps offer personalised experiences with frictionless processes, improving value-added and loyalty.
Time-to-Market: Next-generation solutions are fast to deploy, shortening the time required to build, launch, and scale. In some cases, time to market is reduced by 80%1.
Lower Costs: Next-generation core banking delivers savings up to 50%1 over traditional solutions by simplifying the technology stack, automating operations, paying based on usage. and reducing maintenance.
Regulatory Approval: Regulators in developed markets will not authorise firms unless they can demonstrate their core system is reliable, secure and meets legal and regulatory requirements.
Business Model Agility: Next generation core systems are flexible and easy to adapt. It is possible to innovate new products and operate across borders in a single platform, swapping in/out components and API partners to stay effective.
Core Banking providers in Europe
Sure tracks 40 core banking providers in Europe, with a further 10 early-stage on our watchlist:
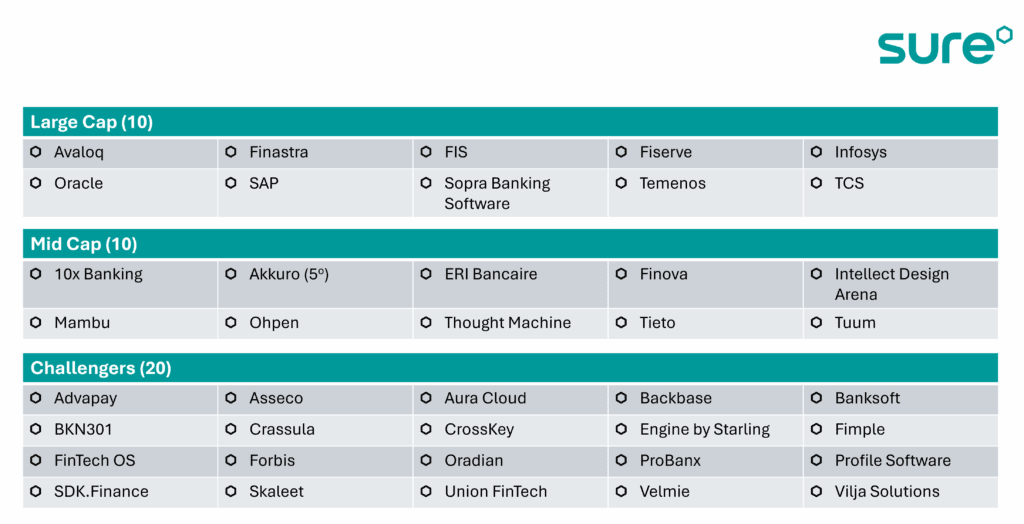
Global providers play a major role due to their scale. Several innovative providers have emerged in the last decade, winning clients and private equity funding, to create a vibrant mid-tier. 20 challengers exist, often with specific product or market specialisms.
Interest in the core banking sector is increasing from financial institutions and private equity investors. The digital transformation of financial services remains relatively low, and as the use cases and benefits of next-generation core banking grow, so do implementations and valuations.